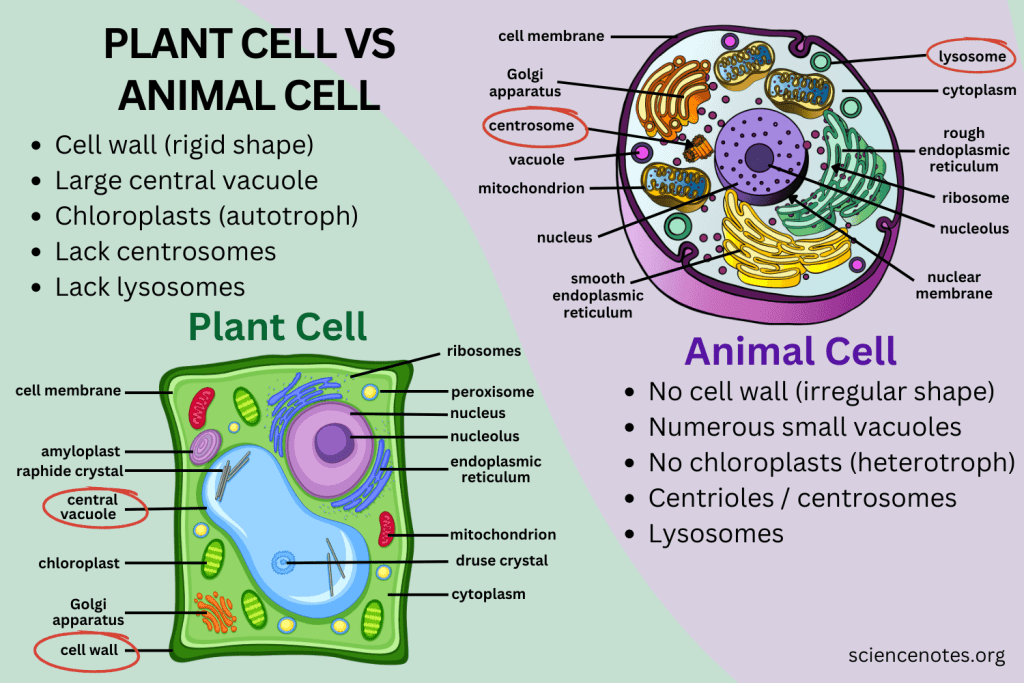
The Cell


DNA is stored in the nucleus, which determines what each cell will become and how they are arranged. Like instructions to build you!
It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and is made of sugar, phosphate, and base. It's shaped like a twisted ladder, called a double helix.
The sides of the ladder are alternating suger and phosphate, and the bases are the rungs.
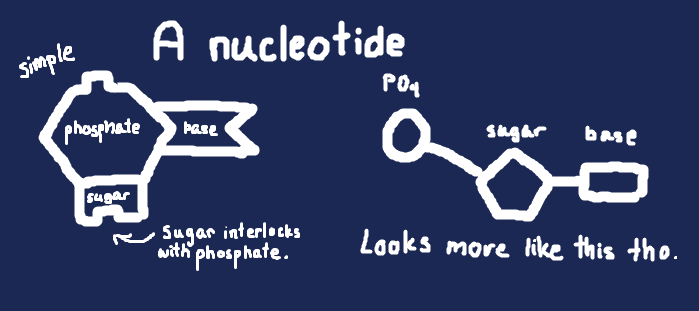
The four bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine (abbreviated with their first letter). A pairs with T and C paits with G (think: A Trait Could Grow).
DNA is usually found in chromatin, which coils during cell division to form chromosomes. Women have XX ones and males have XY.
A gene is a part of the DNA that codes for a protein; similar cells form tissues and similar tissues form organs.
Each X or Y chromosome has two chromatids-- these are called sister chromatids, because they're identical. They're connected by the centromere in the middle. In cases where there is only one chromatid, such as after cell division, each chromatid counts as its own chromosome.
Sexual reproduction requires two parents (or one, for self-pollinating plants.), each providing one gamete (sex cell). Thus, there is a genetic mix between parents.
Advantages include:
Some disadvantages are:
Asexual reproduction is when you clone yourself.
Advantages:There are many forms of asexual reproduction, such as:
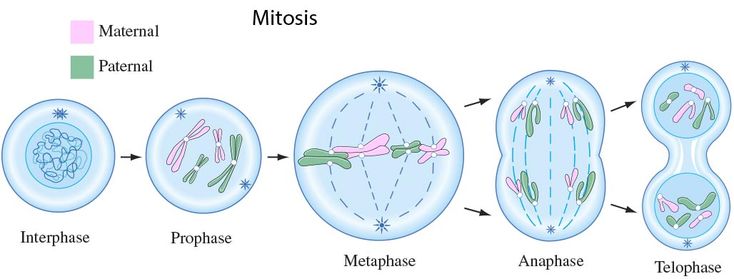
You know when you get a cut and it heals in a few days? You owe that ability to the cell cycle. It's made of three phases: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
The middle section, mitosis, can be further separated into four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. (To remember, you can think PMAT or "Prime Ministers Aren't Trustworthy".)
Here's a diagram to help you.
Meiosis is like mitosis, but doubled. It's used to create gametes, which each have 23 chromosomes instead of 46 (when two join, it forms a full set). Thus, you need to divide twice.
After the first division, there are still 46 chromosomes, but only with one chromatid each. After it is completed there are half as many chromosomes.
